Kirchhoff’s Laws & Circuits
NCERT Chapter 3 (Part 2) • Cells, Networks & Wheatstone Bridge
1. Cells, EMF, and Internal Resistance
EMF (![]() ): The potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of a cell when no current flows through it (open circuit).
): The potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of a cell when no current flows through it (open circuit).
Internal Resistance (![]() ): The finite resistance offered by the electrolyte inside the cell to the flow of current.
): The finite resistance offered by the electrolyte inside the cell to the flow of current.
When a current ![]() is drawn from the cell, the potential difference
is drawn from the cell, the potential difference ![]() is less than EMF:
is less than EMF:
![]() .
.
2. Derivation: Cells in Series
Consider two cells (![]() ) and (
) and (![]() ) connected in series (end-to-end) between points A and C.
) connected in series (end-to-end) between points A and C.
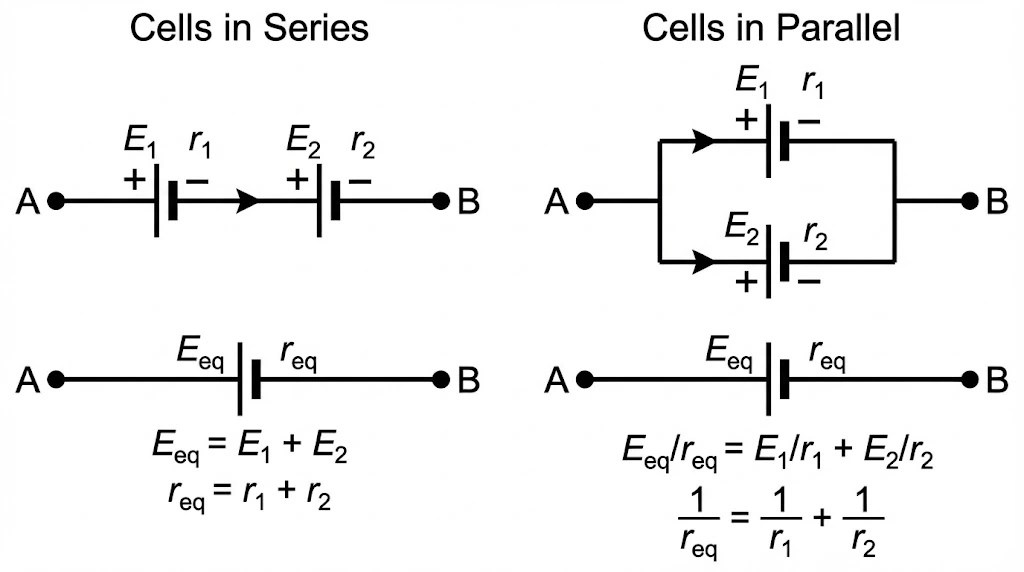
Let
Similarly, for the second cell connected between B and C:
The potential difference across the combination (A to C) is the sum:
Rearranging terms:
If we replace the combination with a single cell of
Comparing the coefficients:
3. Derivation: Cells in Parallel
Consider two cells connected in parallel between points ![]() and
and ![]() . Currents
. Currents ![]() and
and ![]() flow out of the positive terminals.
flow out of the positive terminals.
By conservation of charge (junction rule), the main current
Since they are in parallel, the terminal voltage
For cell 1:
For cell 2:
Substitute
Multiplying by
Comparing this with the standard equation
4. Kirchhoff’s Rules
For complex circuits where Ohm’s law isn’t sufficient, we use Kirchhoff’s Rules.
At any junction, the sum of currents entering equals the sum of currents leaving.
The algebraic sum of changes in potential around any closed loop is zero.
5. Solved Example: Kirchhoff’s Rules
Let’s apply Kirchhoff’s rules to solve a typical circuit problem (Based on NCERT Example 3.6).
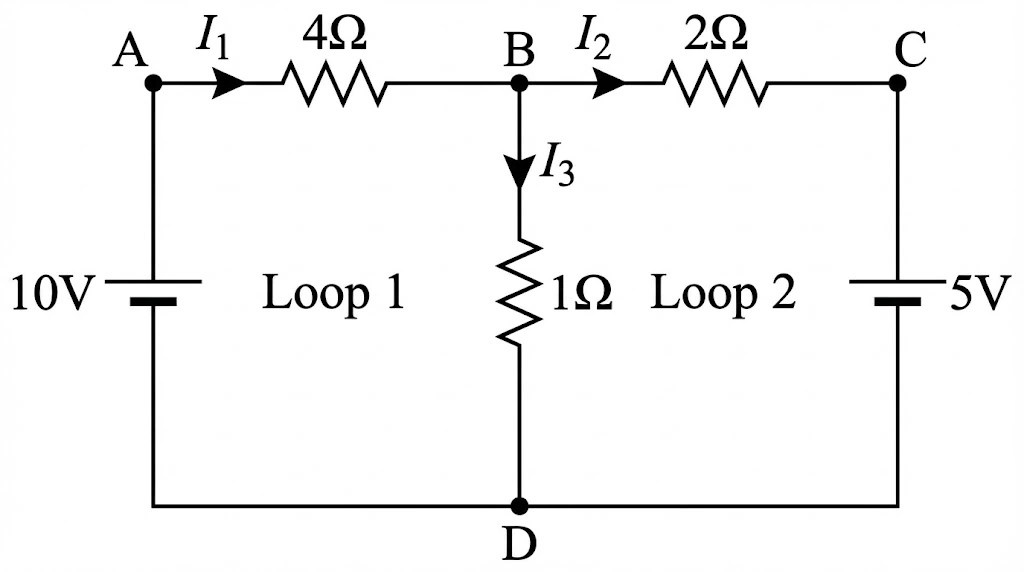
Find currents ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() in the circuit where resistors are
in the circuit where resistors are ![]() and batteries are
and batteries are ![]() .
.
Current entering = current leaving:
Start at A, go clockwise: through 10V battery → 4Ω → 1Ω → back to A.
– Voltage rise: +10V (battery)
– Voltage drop:
– Voltage drop:
So:
Start at B, go clockwise: through 2Ω → 5V battery → 1Ω → back to B.
– Voltage drop across 2Ω:
– Voltage drop across 5V battery: going from **+ to –** → voltage drop →
– Voltage across 1Ω: we’re going **upward**, against
So:
From Equation (1):
Now use Equation (3):
Add Equation (4) and Equation (5):
Plug into Equation (3):
Plug into Equation (1):
6. Wheatstone Bridge
An arrangement of four resistors used to measure an unknown resistance accurately. It consists of four arms (R1, R2, R3, R4) and a galvanometer.

 ).
).Apply loop rule to ADBA (assuming
Apply loop rule to CBDC:
Dividing the two equations:
Ready to test your knowledge? Try 10 solved numericals on Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance: Click here →
Also practice the Question Bank

