Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance
NCERT Chapter 2
Weightage: ~9 Marks
JEE Main: ~2 Qs
Jump To Section:
| Topic | Question Type | Marks |
|---|---|---|
| Derivation: Potential due to Point Charge | Short Answer | 2 Marks |
| Derivation: Potential due to Dipole | Long Answer | 5 Marks |
| Derivation: Parallel Plate Capacitor | Short Answer | 3 Marks |
| Derivation: Energy Stored | Short Answer | 2 Marks |
1. Electric Potential
Electrostatic potential ![]() at a point is defined as the work done by an external force in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point (without acceleration).
at a point is defined as the work done by an external force in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point (without acceleration).
Definition
 SI Unit: Volt (V) = Joule/Coulomb
SI Unit: Volt (V) = Joule/Coulomb
Derivation 1: Potential due to a Point Charge
3 Marks

Step 1: Electrostatic Force
Consider a source charge  at origin. Force on unit positive test charge at distance
at origin. Force on unit positive test charge at distance  :
:

Step 2: Work Done
Work done by external force against this repulsion to move by  :
:

Step 3: Integration
Total work done from  to
to  :
:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com W = -\int_{\infty}^{r} \frac{Q}{4\pi\epsilon_0 (r')^2} dr' = -\frac{Q}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \left[ -\frac{1}{r'} \right]_{\infty}^{r}](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciPjwvc3ZnPg==)
Final Result


Relation between E and V:
Electric field is the negative gradient of potential.
 (Field flows from high to low potential).
(Field flows from high to low potential).
Derivation 2: Potential due to an Electric Dipole
5 Marks

Step 1: Superposition
Potential at P due to  (at
(at  ) and
) and  (at
(at  ):
):

Step 2: Geometry (Cosine Rule)
For  :
:


Step 3: Substitution
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com V = \frac{q}{4\pi\epsilon_0 r} \left[ \left( 1 + \frac{a \cos\theta}{r} \right) - \left( 1 - \frac{a \cos\theta}{r} \right) \right]](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciPjwvc3ZnPg==)

Final Result
Using Dipole Moment  :
:

2. Equipotential Surfaces
An equipotential surface is a surface with a constant value of potential at all points.
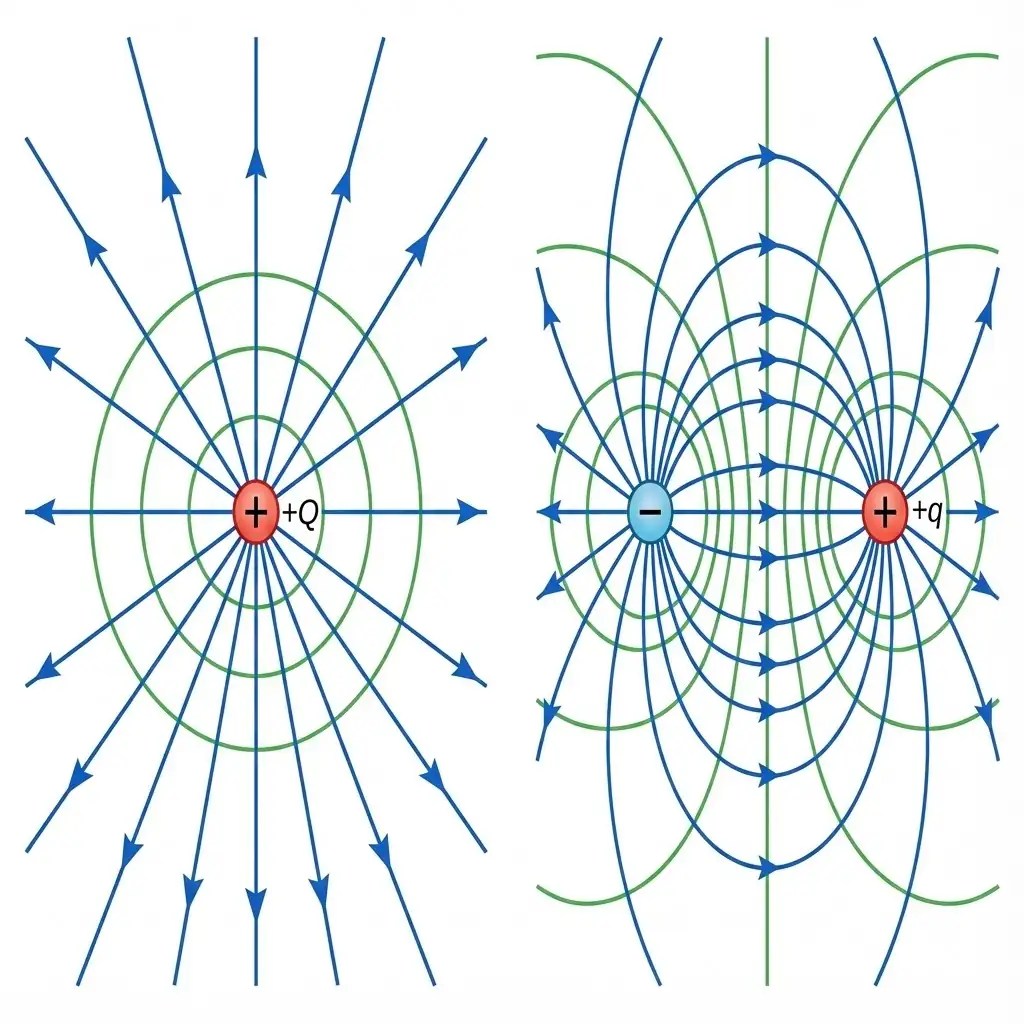
Key Properties
- Work Done: No work is done in moving a test charge over an equipotential surface.
- Field Direction: Electric field is always normal to the equipotential surface at every point.
- Pattern: For a point charge, they are concentric spheres.
3. Potential Energy
Electrostatic potential energy is the work done in assembling a system of charges by bringing them from infinity to their present locations.
Derivation 3: Potential Energy of a System of Charges
3 Marks

Step 1: First Charge
Bring  from infinity to
from infinity to  . Work done
. Work done  (no external field).
(no external field).
Step 2: Second Charge
Bring  from infinity to
from infinity to  . Work is done against field of
. Work is done against field of  .
.

Step 3: Third Charge (Optional)
Bring  against fields of
against fields of  and
and  .
.

Final Result
Total  :
:

Derivation 4: PE of Dipole in External Field
3 Marks

Step 1: Torque
External field  exerts torque on dipole
exerts torque on dipole  :
:

Step 2: Work Done
Work done to rotate dipole from  to
to  :
:

![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com W = pE [-\cos\theta]_{\theta_0}^{\theta_1} = pE(\cos\theta_0 - \cos\theta_1)](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciPjwvc3ZnPg==)
Final Result
Setting reference  (where
(where  ):
):

4. Electrostatics of Conductors
Important Results
- Inside: Electrostatic field is zero everywhere inside the conductor.
- Surface: Electric field is normal to the surface.
- Potential: Constant throughout volume and surface.
- Shielding: Electric field inside a cavity is zero.
5. Capacitance & Dielectrics
Capacitance is the ratio of charge to potential difference: ![]() .
.
Derivation 5: Parallel Plate Capacitor
3 Marks

Step 1: Electric Field
Using Gauss’s Law, field between plates with charge density  :
:

Step 2: Potential Difference
For uniform field  and separation
and separation  :
:

Final Result
Using  :
:

Derivation 6: Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance
3 Marks

Step 1: Polarization
Dielectric polarized creates induced surface charge  .
.
Net field (since
(since  ).
).
Net field
Step 2: Potential

Final Result


6. Combinations of Capacitors
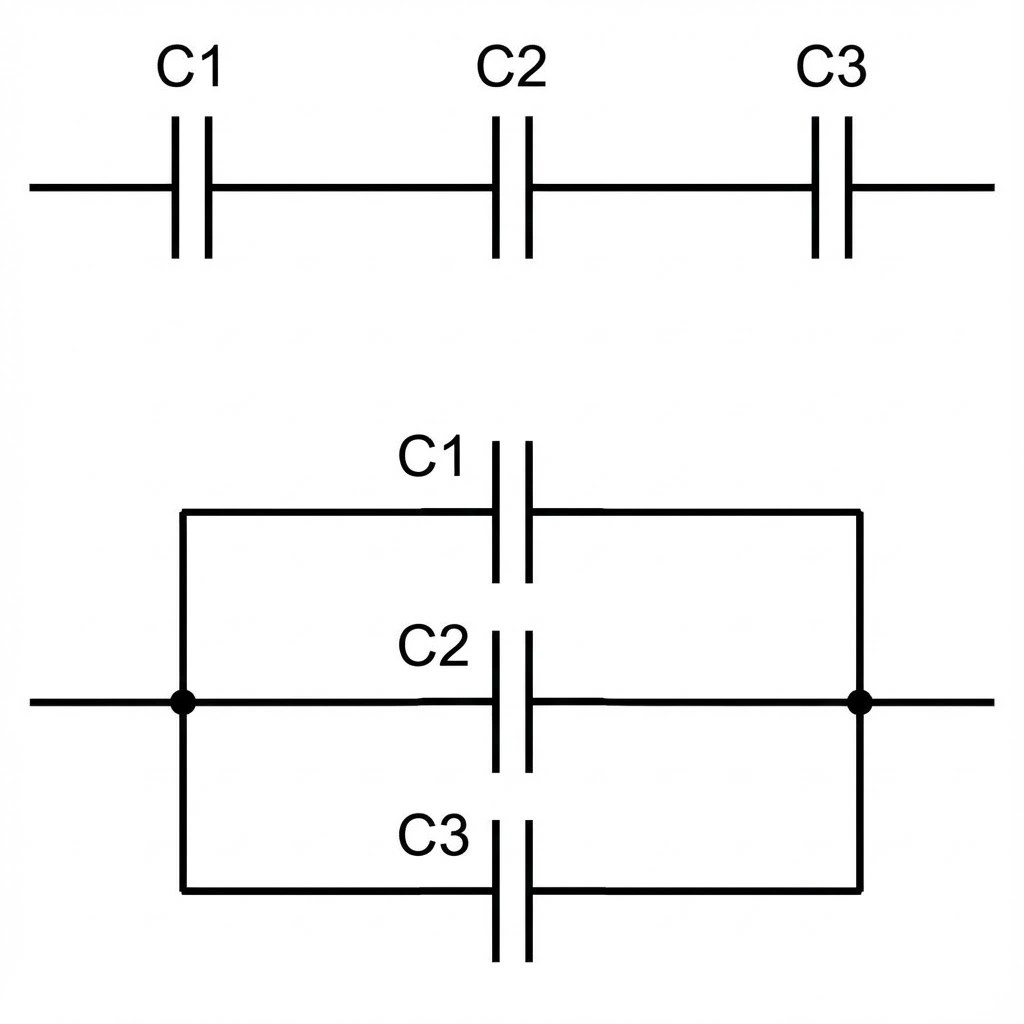
Derivation 7: Capacitors in Series
2 Marks
Logic
In series, Charge (Q) is same on all plates. Potential  divides.
divides.

Substitution

Result

Derivation 8: Capacitors in Parallel
2 Marks
Logic
In parallel, Potential (V) is same. Charge  adds up.
adds up.

Substitution

Result

7. Energy Stored in Capacitor
Derivation 9: Energy Stored
3 Marks
Step 1: Work Done
Work done to transfer infinitesimal charge  against potential
against potential  :
:

Step 2: Integration
Total work to charge from 0 to  :
:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com W = \int_{0}^{Q} \frac{q'}{C} dq' = \frac{1}{C} \left[ \frac{(q')^2}{2} \right]_0^Q](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciPjwvc3ZnPg==)
Final Result

Energy Density:
Energy per unit volume: 
Practice Time!
Ready to test your knowledge? Try 10 solved numericals on Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance: Click here →
Also practice the Question Bank