« Back to AP Physics Guide / Unit 1: Kinematics
AP Physics 1: 1D Motion & The “Big 4” Equations
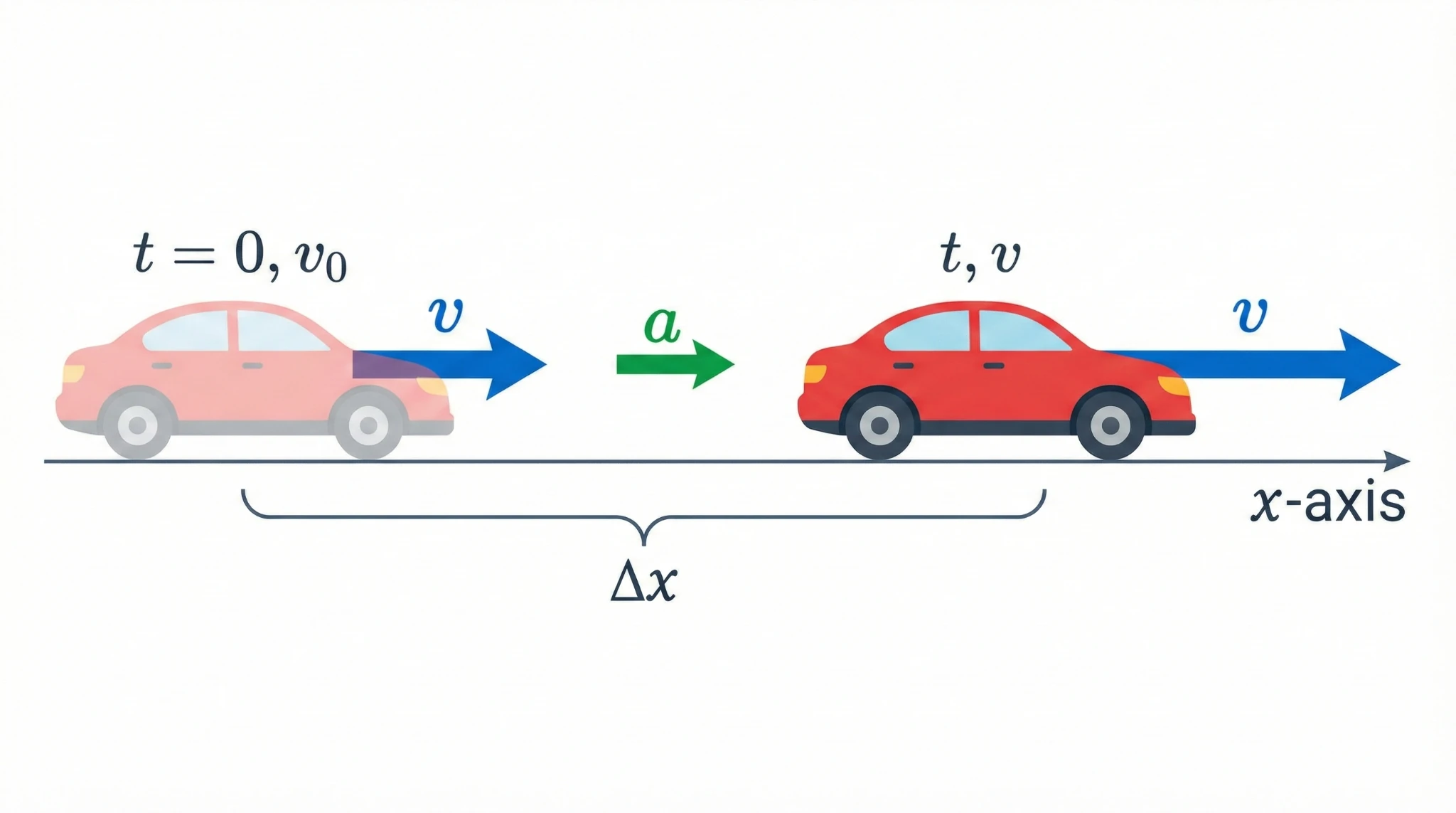
1. The 5 Variables of Motion

Every kinematics problem involves exactly 5 variables. Your first step is always to list them:
 : Displacement (m)
: Displacement (m) : Time interval (s)
: Time interval (s) : Initial Velocity (m/s)
: Initial Velocity (m/s) : Final Velocity (m/s)
: Final Velocity (m/s) : Acceleration (m/s²)
: Acceleration (m/s²)
2. The “Big 4” Equations
These are provided on your AP Formula Sheet. The secret to speed is knowing which variable is missing.
| Equation | Missing Variable? | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Displacement ( |
Finding velocity or time. | |
| Final Velocity ( |
Dropping objects or finding distance. | |
| Time ( |
Stopping distance problems. | |
| Acceleration ( |
Average velocity problems. |
3. Vertical Motion (Free Fall)

 ). Right: Throwing a ball up. Notice that acceleration (
). Right: Throwing a ball up. Notice that acceleration ( ) is always pointing down, even when the ball goes up!
) is always pointing down, even when the ball goes up!When an object is in the air (thrown up or dropped), only gravity acts on it.
Dropping an Object

 (or
(or  on MCQ)
on MCQ)- Displacement
 is negative.
is negative.
Throwing Upward
- Velocity at peak =

- Acceleration is always
 , even at the top!
, even at the top! - Time up = Time down (if landing on same level).
4. AP-Style Practice Question
Question: A car traveling at ![]() applies the brakes and stops over a distance of
applies the brakes and stops over a distance of ![]() . What was the car’s acceleration?
. What was the car’s acceleration?
▶ Click to see Solution
Step 1: List Variables
![]() ,
, ![]() (stopped),
(stopped), ![]() ,
, ![]()
Time (![]() ) is missing!
) is missing!
Step 2: Choose Equation
Use the “Time Independent” equation: ![]()
Step 3: Solve
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
5. Level Up: Harder Practice Problems
Question 2 (Free Fall): A student throws a ball straight up into the air with an initial speed of ![]() . How long does it take for the ball to reach its maximum height? (Assume
. How long does it take for the ball to reach its maximum height? (Assume ![]() )
)
▶ Click for Solution
Key Concept: At the maximum height, the velocity is zero (![]() ).
).
Variables: ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (gravity points down!),
(gravity points down!), ![]()
Equation: ![]()
Solve:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 3 (Symbolic Derivation): A sprinter starts from rest and accelerates at a constant rate ![]() for a time
for a time ![]() . Derive an expression for the final velocity
. Derive an expression for the final velocity ![]() in terms of the distance traveled
in terms of the distance traveled ![]() and the acceleration
and the acceleration ![]() .
.
▶ Click for Solution
Step 1: Identify Knowns
Initial velocity ![]() . Acceleration =
. Acceleration = ![]() . Distance
. Distance ![]() .
.
Note: We need to eliminate time (![]() ) because it is not in the requested answer!
) because it is not in the requested answer!
Step 2: Choose Equation
Use the time-independent equation: ![]()
Step 3: Solve
![]()
![]()