Impulse is defined in physics as the force over time describing the change in the motion of an object. It is one of the most crucial concepts in explaining the phenomenon involved in such interactions as that of a car crash or a basketball moving through the air. The following shall present the impulse, formula, and examples on its application in real-world problems.
What is Impulse meaning in Physics?
It’s the change in momentum produced when a force has an opportunity to be applied over some interval of time in physics. A very proper word is, perhaps, one measuring how an applied force affects the body within some time span.
The quantity known as impulse is vector, it does have not only a magnitude but also a direction.
Formula for Impulse
The mathematical expression for impulse is:
![]()
Where:
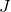 : Impulse (N·s)
: Impulse (N·s)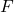 : Force applied (N)
: Force applied (N)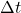 : Time duration of the force (s)
: Time duration of the force (s)
Alternatively, impulse can also be expressed in terms of momentum:
![]()
Where:
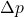 : Change in momentum (kg·m/s)
: Change in momentum (kg·m/s)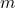 : Mass of the object (kg)
: Mass of the object (kg)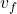 : Final velocity (m/s)
: Final velocity (m/s)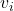 : Initial velocity (m/s)
: Initial velocity (m/s)
You may also like to know about Fluid Mechanics
Understanding Impulse with Examples
Example 1: Collision of Two Objects
During a car crash, the impact force is applied for a very short time. The impulse experienced during the crash determines the change in momentum of the car and, therefore, the severity of the collision.
Example 2: Sports
For example, in sports, impulsive is when one smashes the ball using a bat or racket. The force developed due to the short period of contact changes the velocity of the object, in this case, the ball.
Impulse vs. Momentum
Impulse and momentum seem almost related but are actually different. Momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object, p = mv. Impulse describes the change in momentum.
Applications of Impulse in Real Life
- Car Safety Features
Seat belts, airbags, and crumple zones are all designed to spread out the time of impact upon impact, therefore reducing force and injury. - Rocket Propulsion
The launches of rockets apply impulse. This refers to the manner through which the force from the engines of the rockets changes the rocket’s momentum over time. - Sports Strategies
Sport athletes can use impulse as a way of optimization in techniques. This implies maximizing the force and time of contact to improve performance.
Table: Key Differences Between Impulse and Momentum
| Aspect | Impulse | Momentum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Change in momentum | Product of mass and velocity |
| Formula | ||
| SI Unit | Newton-second (N·s) | Kilogram-meter per second (kg·m/s) |
| Nature | Vector quantity | Vector quantity |
| Physical Context | Explains the effect of a force over time | Describes the state of motion |
Sample Calculation: Impulse in Physics
Problem:
A 2 kg ball is initially moving at 3 m/s. A force of 10 N is applied to the ball for 0.5 seconds. Find the impulse and the ball’s final velocity.
Solution:
Calculate the impulse:
![]()
Calculate the change in velocity using ![]() :
:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Answer: The impulse is 5 N·s, and the final velocity is 5.5 m/s.
Importance of Impulse in Physics
Understanding impulse has significant implications in both theoretical physics and practical applications. It provides insight into how forces affect motion and helps design systems to control or enhance these effects.
Table: Common Scenarios Involving Impulse
| Scenario | Impulse Role |
|---|---|
| Car crashes | Reduces injuries by increasing impact duration |
| Sports (e.g., tennis, golf) | Changes velocity of the ball to achieve desired direction and speed |
| Rocket launches | Provides momentum to overcome gravitational pull |
| Martial arts | Maximizes force delivered in a strike |
Conclusion
Impulse is a crucial concept in physics that bridges the gap between force and motion. Its applications span diverse fields, from automotive safety to sports and aerospace engineering. By understanding the meaning and formula of impulse, practical problems involving forces and momentum can be effectively analyzed and solved.
Optimize for Impulse in Everyday Scenarios: Whether it’s understanding the impact of a crash or improving athletic performance, the principle of impulse is integral to making informed decisions.